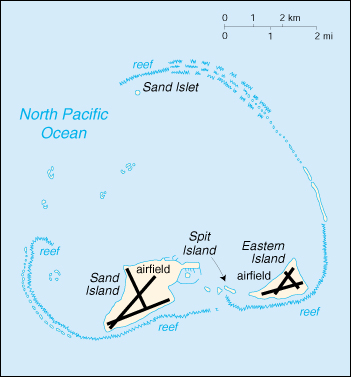
| The
Midway Islands consist of a circular atoll, 6 miles in diameter,
enclosing two islands. Lying about 1,150 miles west-northwest
of Hawaii, the islands were first explored by Captain N. C.
Brooks on July 5, 1859, in the name of the United States. The
atoll was formally declared a U.S. possession in 1867, and in
1903 Theodore Roosevelt made it a naval reservation. The island
was renamed “Midway” by the U.S. Navy in recognition of its
geographic location on the route between California and Japan.
Air traffic across the Pacific increased the island's importance
in the mid-1930s; the San Francisco–Manila mail route included
a regular stop on Midway. Its military importance was soon recognized,
and the navy began building an air and submarine base there
in 1940. The Battle of Midway, which took place from June 3–6,
1942, was considered a turning point in World War II. After
the war, the strategic importance of the island declined; the
Midway stop for commercial air traffic was eliminated in 1950,
and the air base closed in 1992. Midway served as an U.S. Naval
Base until 1996, when Midway Phoenix Corporation and the United
States Fish and Wildlife Service entered into a cooperative
agreement under which this pristine National Wildlife Refuge
is now available as a travel destination. A coral atoll is open
to the public for wildlife-related recreation in the form of
wildlife observation and photography, sport fishing, snorkeling,
and scuba diving. The economy is based on providing support
services for the national wildlife refuge activities located
on the islands. All food and manufactured goods must be imported.
Die
Midway Islands bestehen aus einem runden Atoll, 6 Meilen im
Durchmesser, das zwei Inseln umfasst. Etwa 1,150 Meilen west-nordwest
von Hawaii gelegen, wurden die Inseln im Namen der Vereinigten
Staaten erstmals von Kapitän N.C. Brooks am 5. Juli 1850
erforscht. Das Atoll wurde 1867 offiziell zum Besitz der USA
erklärt, und 1903 gründete Theodore Roosevelt dort
eine Niederlassung der Marine. Die Insel wurde von der Marine
in "Midway" umbenannt, in Anerkennung seiner geographischen
Lage auf der Route zwischen Kalifornien und Japan. Der Luftverkehr
über den Pazific erhöhte die Bedeutung der Insel in
der Mitte der 1930er Jahre. Die Postroute San Francisco - Manila
beinhaltete einen Stop auf Midway. Seine militärische Bedeutung
wurde schnell erkannt, und die Marine begann 1940 mit dem Bau
eines Luft- und U-Bootstützpunktes. Der "The
Battle of Midway" (3. bis 6. Juni 1942) gilt als ein Wendepunkt
im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Nachdem Krieg nahm die strategische Bedeutung
der Insel ab. Die Landung auf Midway bei kommerziellen Flügen
wurde 1950 abgeschafft, und der Luftwaffenstützpunkt 1992
geschlossen. Midway blieb als U.S. Naval Base bis 1996 geöffnet.
Danach schlossen die Midway Phoenix Corporation und der United
States Fish and Wildlife Service eine gemeinsame Vereinbarung,
unter der dieser unberührte Naturparkt als Reiseziel zugänglich
ist. Ein Korallenatoll ist der Öffentlichkeit zugängich
für Freizeitaktivitäten wie Tierbeobachtung und Fotografie,
Sportfischen, Schnorkeln und Tauchen. Die Wirtschaft begründet
sich in der Zulieferung von Diensten für das Tierschutzgebiet.
Alle Lebensmittel und Güter müssen importiert werden.
STATISTICS
Population (April 2003 est): no
indigenous inhabitants; approximately 40 people make up the
staff of US Fish and Wildlife Service and their services cooperator
living at the atoll
Land Area: 2
sq. mi. (5 sq. km)
|